EVAP, which is a shortened name for Evaporative Emission Control System, is a mechanism used in an engine to prevent the leaking of gasoline vapors from the fuel system and fuel tank into the atmosphere.
The EVAP system is built in a way that it doesn’t need constant maintenance, but occasional damages can happen and turn the check engine light on. There is also a possibility of a vehicle failing in an OBD II plug-in emission test.
On vehicles that are made in 1996 or more current, the OBD II EVAP monitor will have an ability to self-check the fuel vapor leaks. If the automatic system finds any leaks, whether they are caused by loose gas caps, the check engine light will be turned on to signify a problem. But, this monitoring system will only run if certain conditions are met. A problem that can occur from this is that vehicle owners can fail an OBD II plug-in emission test from the failure of proper checking by the monitor.
The main problems that occasionally occur with EVAP systems include a variety of reasons, including the faulty purge valve that causes unwanted leaks to the engine, damaged vacuum hoses, and also an incorrect installation or sizing on gas caps. P0440 is the most common fault code, which means that there is a large vapor leak, normally caused by an unfit gas cap. Other common codes include P0443 to P0449.
One code that is hard to solve is P0442. This code is a notice about a small leak in the fuel system, but they are usually the leading cause for other bigger problems. Small leaks are hard to notice, even with thorough inspections. Therefore, the usage of special testers such as smoke machines will be needed for this. This machine will insert some type of mineral-based vapor into the fuel system. A minuscule amount of pressure will also be applied during the process. An ultraviolet dye may also be used to help see the pinprick leaks.
If the EVAP system shows fault code, whether it’s P0442 or the others, it might be wiser to call professional technicians for the job, as fixing them can be quite challenging.

Why EVAP?
EVAP is required by the EPA because of concerns about smog that is produced by cars. The gasoline used by cars contains different types of hydrocarbons. These hydrocarbon substances can react with air and sunlight, which in turn create dangerous smog. Gasoline contains aldehydes, olefins, aromatics, and paraffin. Some of them can even instantly reach with air and heat to create smog that pollutes the air.
Regulation is needed because fuel vapors are produced from cars even when they are not being driven. If somehow the fuel system is left open, the vapors will pollute the air for 24 hours without being controlled. Leaks like this actually account for around 20 percent of air pollution caused by motorized vehicles.
The solution from EVAP works well because the system will seal off fuel vapors from the tank and reroute them into the EVAP storage canister. The vaporized chemicals will then be stored in the canister until the engine is restarted. The mechanism then continues when the engine is warm enough by releasing the vapors back into the intake manifold. The running engine will then burn off these excess vapors.
Since the first time it was applied on cars in 1970, the EVAP system has been used on every piece of cars and trucks being produced to this day.
How the EVAP Works
For the fuel system to work, the engine needs to let air in. The air has a function to replace the space left by fuel when they are being used. Otherwise, there will be a negative suction pressure as the engine empties and burns off fuel, which could lead to the collapse of the fuel tank. Without EVAP, this mechanism of letting air in can also let fuel vapors go out. EVAP works by eliminating the possibility of leaks by venting the vapors to specialized canisters.
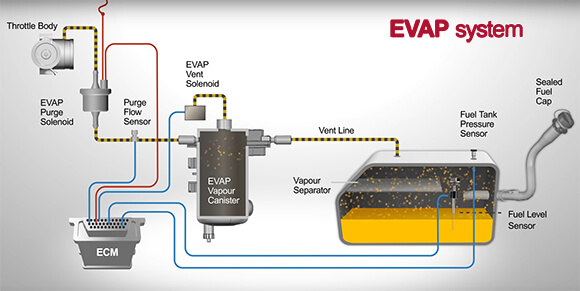
EVAP System Components
Some main components of EVAP include:
Fuel tank, which has an empty space around the top to accommodate extra volume when fuels expand during hot weather. This space can prevent the overflowing of fuel and reduce the risk of leaks.
Gas cap, that in newer vehicles it will be sealed completely. Different situations might apply for cars that are produced pre-OBD II. Please note that when changing the gas cap, make sure to get the same type as before.
Liquid-Vapor Separator, which is located around the top part of the tank. This device has a function to prevent liquid fuel from entering the EVAP canister. Without it, liquid fuel can fill the canister faster than it should, rendering the EVAP system to be less efficient in trapping fuel vapors. While liquid-vapor separators are generally easy to maintain, damages can still happen on them. For instance, the vent might get blocked with residue or rust, or metal fatigues could arise from the engine vibration.
A different approach is also used by some liquid-vapor separators by using a simple mechanism of float and needle. If fuel level is above where it should, the float will rise and activate the valve to close the vent line.
Some manufacturers also use foam on the top of the fuel to trap excess liquid fuel and prevent them from entering the vent.
The connection between the tank and the EVAP canister can also get blocked for many reasons. You can notice this by the soft whooshing sound when you open the fuel tank. This problem needs to be fixed quickly because it could cause fuel starvation or even the fuel tank to collapse. The solution is to temporarily disconnect the vent line from the canister, and then blow some air into the tank. If there is no blockage, air should be able to travel free. If there is, clean the vent line or replace it with a new one.
EVAP Canister, which is a small storage space made from plastic or metal, located somewhere in a corner of the engine compartment. Activated charcoal is normally used to absorb and store vapors from the fuel. Activated charcoal is also used due to the long lifespan, which makes them last for the lifetime of your vehicle. They work by temporarily storing the vapors and use the heat from the engine to turn vapors back into burnable fuels. The vent line connects the charcoal canister with the fuel tank, and that’s why it needs to be kept clean at all times.
While EVAP Canister can last a long time, some problems that can occur on them include the faulty purge control. To check this, a vacuum pump can be used to apply vacuum pressure inside the purge valve. If the valve stays closed during inspection, then the canister is good. Solenoid-type purge valves can be checked using an ohmmeter to see the chance of it being shorted.
Experts should always be called when EVAP systems run into problems because some diagnostic procedures can get really complicated and hard to fix without proper training and knowledge.
Evaporative Emissions & OBD2
OBD2 systems are applied on vehicles that were produced in 1996 and more recent. This system is placed to ensure that there are no dangerous chemicals getting released into the free air. The EVAP monitor reaches this goal by two measures: by verifying that the airflow from EVAP canister to the engine is unobstructed, and by ensuring that the fuel tank and fuel system are free from leaks.
OBD2 EVAP system will only run one in a drive cycle by first checking the fuel level in the tank. It will only run when the fuel level is between 15 to 85 percent. Meanwhile, the EVAP monitor will also detect leaks by using a “purge flow sensor”. On cars produced between 1996 to 1999, the minimum size of detectable leak is .040 inches in diameter, and around 0.020 inches for most newer models.
EVAP Fault Codes
When the detection mode is running, the EVAP will show fault codes as a way to recognize the problems. The code ranges from P0440 to P0457, and their meanings are:

If the EVAP monitor shows code P0440, P0455, or P0457, the solution can be as easy as tightening the gas cap back. You can do this by removing the gas cap and then check the condition of the filler tank inlet seal. There might also be some debris or deposits under the gas cap. Clean the cap and put it back on. Make sure you hear a soft clicking sound as a sign of a tight seal on the tank. After doing this, the fault code should be cleared the next time you turn the engine on. But if the vehicle’s check engine light still comes on, the problem might be caused by an unfit gas cap, or a large vapor leak in the vapor suction mechanism.
Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detection
Leak detection is a difficult job to do on the EVAP system. The main requirement is a specialized smoke machine that can produce mineral-based light smoke at a very small pressure point. The pressure will push the smoke around the line to reveal leaks too small for normal sight. The visibility of leaking smoke can also be improved with the use of ultraviolet light.
